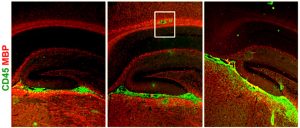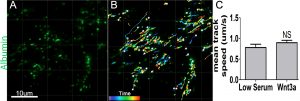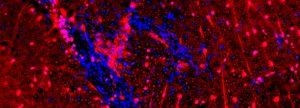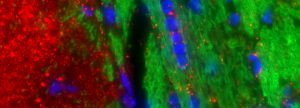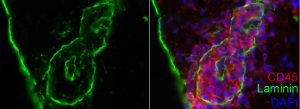
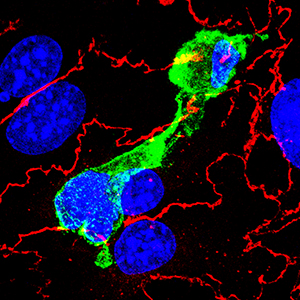
T cells (green) squeeze through blood-brain barrier endothelial cells (red).
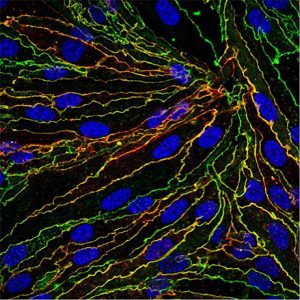
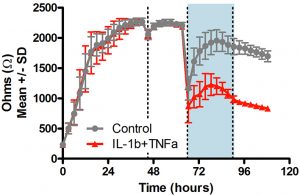
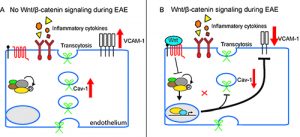 Endothelial cell Wnt/b-catenin activation protects the neurovascular unit in the EAE model of multiple sclerosis. A) In the absence of Wnt signaling, neuroinflammation is exacerbated by elevated caveolar transcytosis and vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM-1) expression. B) Wnt/β-catenin mediated transcription suppresses caveolar transcytosis and VCAM-1 expression, markedly reducing T cell infiltration into the CNS.
Endothelial cell Wnt/b-catenin activation protects the neurovascular unit in the EAE model of multiple sclerosis. A) In the absence of Wnt signaling, neuroinflammation is exacerbated by elevated caveolar transcytosis and vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM-1) expression. B) Wnt/β-catenin mediated transcription suppresses caveolar transcytosis and VCAM-1 expression, markedly reducing T cell infiltration into the CNS.